Blog
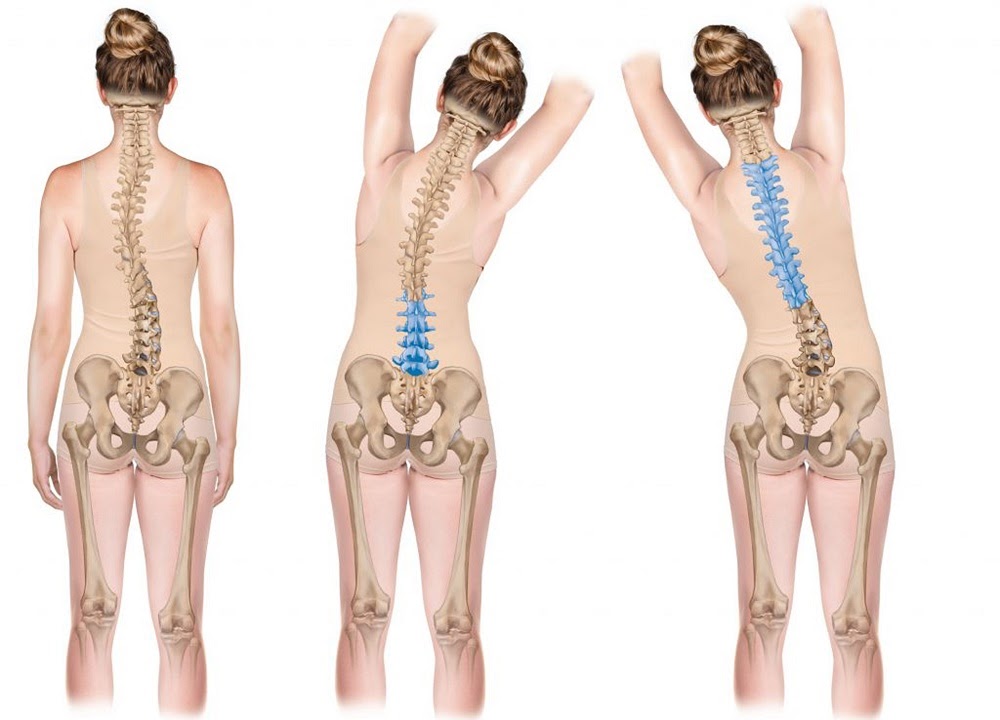
What is Schroth Therapy for Scoliosis?
Schroth therapy is a method of positioning, stretching and strengthening activities that are specifically designed to treat scoliosis. In the past, research has found that typical exercise plans of generalized strengthening and/or chiropractic adjustments are ineffective for the treatment of scoliosis. This is because scoliosis is an imbalance of strength on either side of the spine.
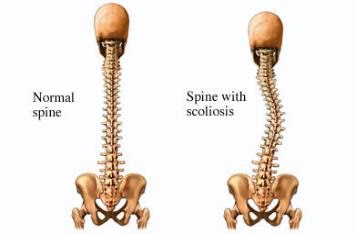
Identifying and Targeting Areas for Schroth Therapy
In order to correct this imbalance, it is necessary to identify and target the weaker areas and strengthen them in order to aid in the realignment of the spine.
Schroth differs from other strengthening programs, in that is addresses the multidimensional mechanisms of scoliosis. Since scoliosis results in misalignment of the spine in all 3 anatomical planes, it is important that all three planes be addressed in treatment.
Schroth therapists are trained intensively on how to identify different types and stages of scoliosis in order to correctly prescribe the appropriate stretching and strengthening activities for each individual child. Every case of scoliosis is different, so every treatment plan is individualized for optimal results.
Schroth therapy is considered a conservative treatment, where the goal is to both correct the spinal alignment, as well as avoid more invasive treatments like bracing or surgery. It is effective for both mild and severe curves, in children of all ages. Children participating in Schroth therapy can be expected to have 1 hour sessions, 1-3 times a week. Both children and parents will be fully educated on the mechanisms of scoliosis, as well as the specific type and severity of scoliosis that they have been diagnosed with.
Treatments Commonly Paired With Schroth Therapy
Schroth therapy is a comprehensive approach to scoliosis treatment that can be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as bracing or surgery. It is often used as a first-line treatment for scoliosis in children and adolescents, and it can also be used to help adults with scoliosis manage their symptoms.
- Bracing: Bracing is a common treatment for scoliosis. A brace is worn to help keep the spine in alignment and prevent the curve from progressing. Schroth therapy can be used in conjunction with bracing to help improve the alignment of the spine and make the brace more effective.
- Surgery: Surgery is sometimes recommended for scoliosis, especially in cases where the curve is severe or is causing pain. Schroth therapy can be used before or after surgery to help improve the alignment of the spine and make the surgery more successful.
- Stretching: Stretching can help to improve the flexibility of the spine and make it easier to correct the curve. Schroth therapy often includes stretching exercises, and it can be used in conjunction with other stretching exercises to help improve the alignment of the spine.
- Strength training: Strength training can help to strengthen the muscles that support the spine. This can help to prevent the curve from progressing and improve the patient’s overall posture. Schroth therapy often includes strength training exercises, and it can be used in conjunction with other strength training exercises to help improve the alignment of the spine.
- Postural awareness: Postural awareness is the ability to be aware of your body’s alignment and make adjustments to improve it. Schroth therapy teaches patients how to improve their postural awareness, and it can be used in conjunction with other treatments to help improve the alignment of the spine.
Other topics that will be addressed are likelihood of progression and reasonable expectations for correction. Exercises and stretches will also be given for homework, so that therapy is able to extend beyond the hours in the clinic. The Schroth method’s efficacy is also in part due to its family centered and patient focused views.
We believe that when the family, the child and their Schroth therapist all work together, the patient’s potential for scoliosis correction is maximized.
Give us a call at (815) 469-1500 or Get Started Here.




